The Unknome project
The human genome encodes ~20,000 proteins, many still uncharacterised. Scientific and social factors have resulted in a focus on well-studied proteins, leading to a concern that poorly understood genes are unjustifiably neglected. To address this, we have developed an “Unknome database” that ranks proteins based on how little is known about them.
The database is intended to aid the selection of poorly characterised proteins from humans or model organisms so that they can be targeted for investigation. We welcome feedback! Please email Tim Stevens tstevens@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
The current version of the Unknome database (updated 18 Oct 2024) represents 15,657 proteins from 142 species grouped into 15,657 Panther families. These are linked to a total of 11,540,683 Gene Ontology annotations. The previous version of the Unknome data is available by clicking here; any other open pages will need to be reloaded to reflect this.
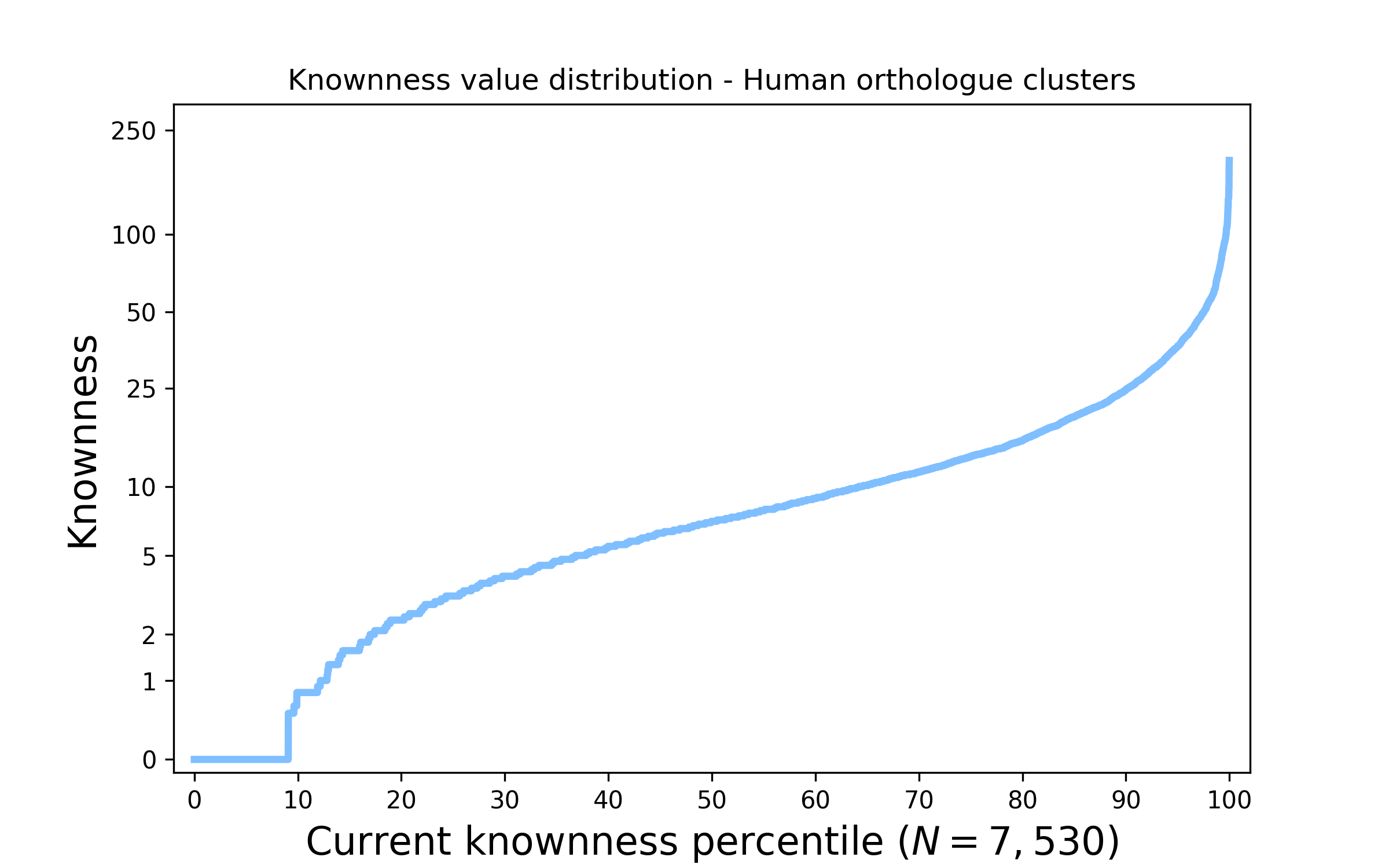
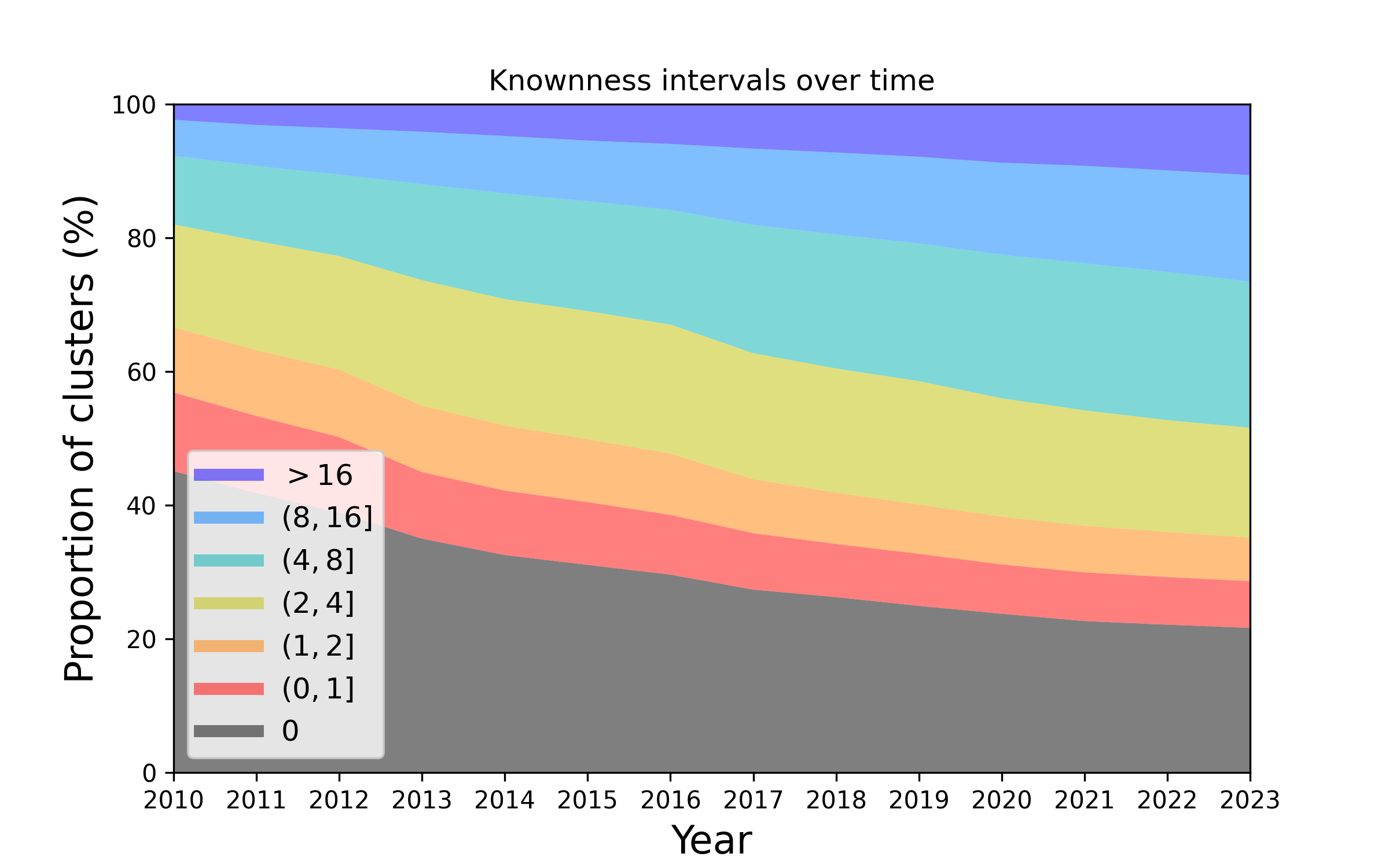
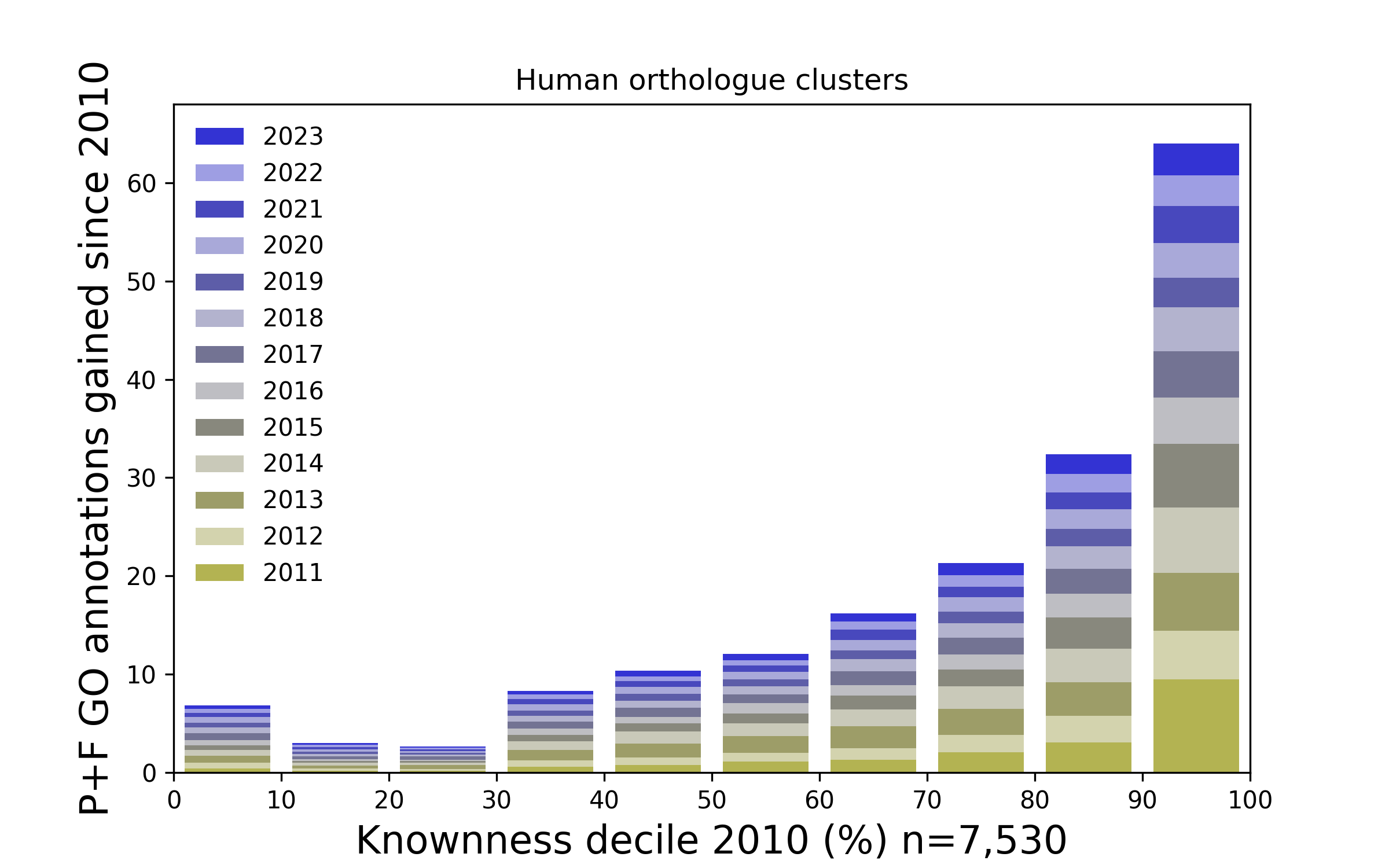
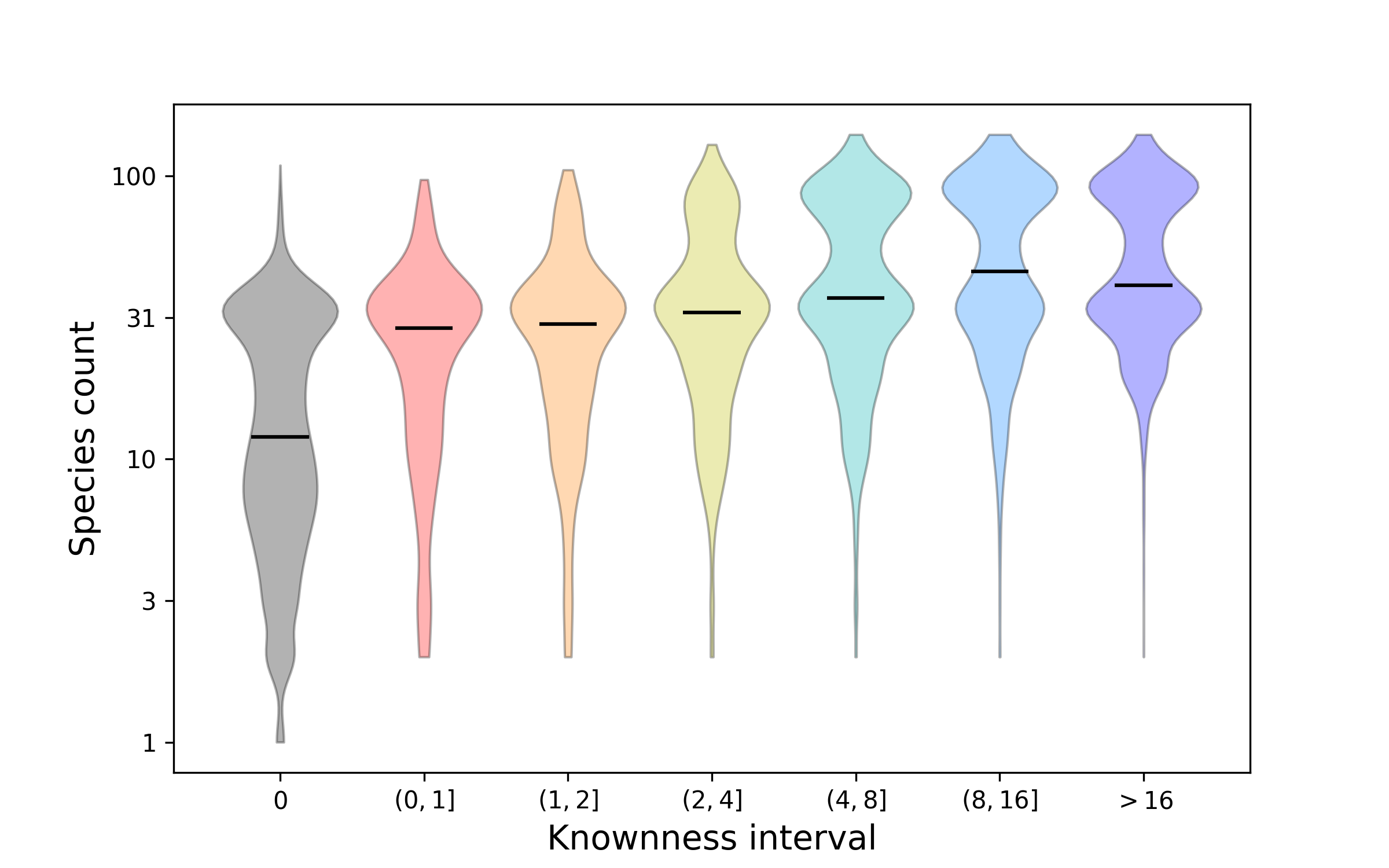
See this page for a graphical summary of the Unknome database.
Citation and Contributors
The Unknome database is described in this publication, along with our application of it to investigate in Drosophila a set of poorly understood proteins:
Functional unknomics: Systematic screening of conserved genes of unknown function
Joao Rocha, Satish Arcot Jayaram, Tim J Stevens, Nadine Muschalik, Rajen D Shah, Sahar Emran, Cristina Robles, Matthew Freeman, Sean Munro
PLoS Biol. 2023 Aug; 21(8): e3002222
PMID: 37552676
Technical details
The overall principle of the unknome database is to assign a knownness score to proteins. Each protein is placed in a cluster of orthologues based on the Panther database. The knowness score is defined as the largest number of Gene Ontology (GO) terms that has been assigned to a member of that cluster. Because GO annotations vary in confidence and relevance to function, different types of evidence can be assigned a different weight when calculating the score. The list of scored clusters can also be restricted to those containing proteins from humans and/or the main model organisms.
See the Ranked Clusters section for a list of protein clusters ranked by their knowness score with links to further information on the cluster and the proteins it contains.
See Cluster search for information about each cluster showing the GO terms assigned to its members, and how its knowness has changed over time.
Settings shows the weights applied to different types of GO annotation. Our default settings give most weight to manual curation and experimental evidence. We excluded 'Cellular component' as a Domain as it provides limited functional information. It is possible to alter these settings and calculate a custom unknome, but be patient!
The data that goes into the Unknome database and website is derived from:
- UniProt : For proteome sequences, protein annnotations and inter-resource cross-references.
- Panther DB : For the grouping of proteins into orthologous groups across many eukaryote species.
- Gene Ontology : For molecular function and biological process annotaions of gene products.
Unknome Downloads
The current version of the Unknome database may be downloaded as:
- A summary table for all proteins: tab-separated text Gzip compressed file (54.2 MiB) or uncompressed file (252.6 MiB)
- A summary table for all orthologue clusters: tab-separated text Gzip compressed file (2.8 MiB) or uncompressed file (8.0 MiB)
- The entire relational database: SQLite3 file (5.3 GiB)
See the download table to obtain files for previous database versions.